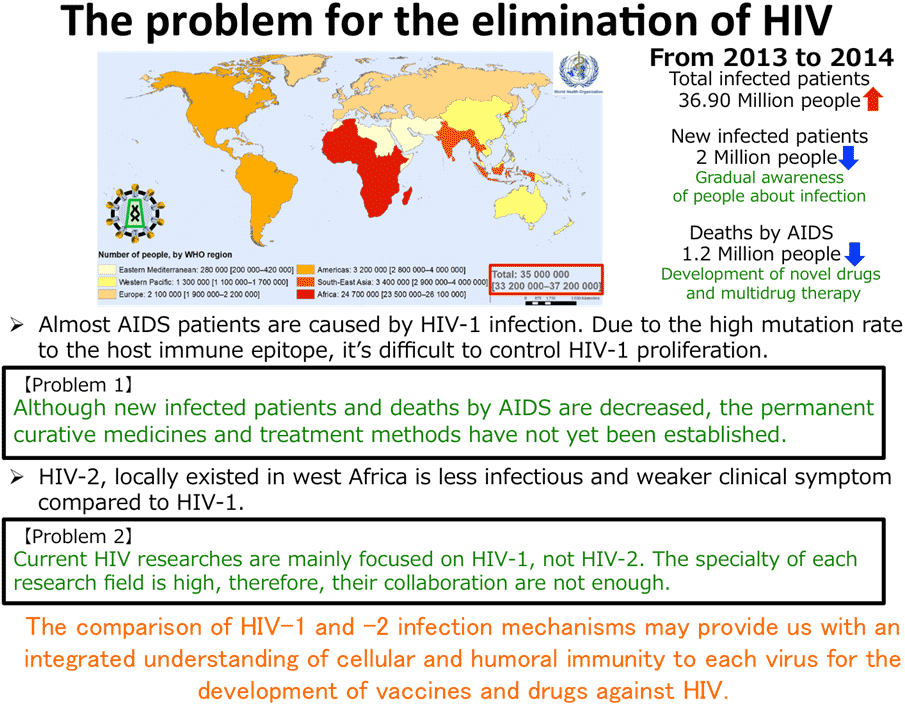
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) causes Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Although the development of anti-viral drugs and clinical technologies have continued, permanent curative medicines and treatment methods have not yet been established. During the early stages of infection, HIV and HIV infected-CD4 positive T cells are eliminated by cytotoxic T cells (CTLs), Natural Killer cells (NK cells) and neutralization antibodies that bind to HIV proteins such as the viral surface envelope glycoprotein (Env). But HIV can escape from host`s immune system by mutations in HIV proteins during proliferation. In contrast to HIV-1, the related virus HIV-2 rarely causes AIDS because the HIV-2 infected individuals have lower levels of viral load and slower rate of clinical progression characterized by a longer asymptomatic stage. The majority of HIV research is focused on HIV-1 due to the high transmission rate. Even so, the comparison of HIV-1 and -2 infection mechanisms may provide us with an integrated understanding of cellular and humoural immunity to each virus for the development of vaccines and drugs against HIV.
We have already started collaborations (through the student internship program) with the department of medicine of Oxford University. This project further expands the collaboration to research areas of focus in the respective universities (e.g. structural biology and various screening tools for drug discovery in Hokkaido University, and clinical genetics and next generation structural analysis methods in Oxford University). These collaborations help to bring understanding to the infection mechanisms of HIV and the development of peptide vaccine and drugs that activate both cellular and humoral immunities. At the same time, this project also grows researchers who are familiar with advanced technologies and methods. These researchers build the international research network from the aspect of both immunity and infection, and, finally, Hokkaido University can be the basement of the drug discovery against virus, bacteria and other infectious microbes.
